Master Attribution Modeling with this practical guide. Learn to choose and implement the right model to prove marketing ROI and drive real revenue growth.
Attribution modeling is the framework for figuring out which marketing touchpoints a customer actually engaged with on their winding path to becoming a customer. Instead of just guessing which channels are working, you get a data-driven map showing the true impact of everything from the first ad they saw to the final demo they booked. This is how you stop wasting money and start proving marketing's real contribution to the bottom line. For RevOps leaders, mastering attribution isn't optional—it's the only way to build a predictable revenue engine.
Moving Beyond the Last-Click Delusion
Are you tired of the guessing game? So many SaaS companies are still flying blind, clinging to the simplistic "last-click" attribution model. It’s like a detective solving a year-long case and giving all the credit to the final clue found at the crime scene, completely ignoring the months of stakeouts, interviews, and forensic work that led to the breakthrough.
That’s a dangerously incomplete picture.
When you only credit the final touchpoint—that "request a demo" form fill—you completely ignore the blog posts, social ads, and webinars that guided your prospect through their entire journey. This creates a massive visibility gap. You end up overvaluing bottom-of-funnel activities while starving the crucial top-of-funnel efforts that create demand in the first place. This is the perception-reality gap that kills marketing budgets. As Jay Famico, a former Forrester analyst, puts it, "Last-click is popular because it’s easy. It’s also wrong."
The Real Cost of Flawed Attribution
When your attribution is broken, the consequences ripple across the entire business. You're left unable to confidently answer the most basic questions:
- •Which campaigns are actually generating qualified pipeline?
- •What’s the true ROI of our content marketing?
- •Where should we put our next marketing dollar for the biggest impact?
This locks you into a cycle of reactive, gut-feel decisions instead of building a proactive, data-driven strategy. To really break free, you have to address issues like unclear channel attribution, which is the key to unlocking real insight into your customer journeys. Without that clarity, you're not just flying blind; you’re actively rewarding the wrong channels.
A Global Shift Towards Clarity
This isn't just some hypothetical problem; it's a global business imperative. In the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) market, for instance, the move to multi-touch attribution has taken off as businesses pour more budget into digital channels. A 2025 industry analysis projected the GCC marketing attribution software market would hit approximately USD 410 million, a surge driven by the urgent need to understand complex, omnichannel journeys. This isn't a regional quirk—it's a worldwide trend away from guesswork and toward a precise understanding of the path to revenue.
Ultimately, getting attribution right is about shifting your entire organization’s mindset. It’s the move from, "We think this LinkedIn campaign works," to, "We know this campaign drives a 15% lift in SQLs with a 90-day payback period." This is the first, non-negotiable step toward building a predictable revenue engine.
Choosing the Right Attribution Model for Your Business
Picking an attribution model isn't just a technical task—it's a strategic decision that dictates where you point your marketing budget. Get it wrong, and it’s like using a city map to navigate the ocean. You’re using the right kind of tool for the completely wrong journey, and your budget decisions will be disastrously off-course.
Forget the dry, academic definitions for a second. The real question is this: what business goal are you trying to hit right now? The answer will tell you which model gives you the clearest picture of reality.
Single-Touch vs. Multi-Touch Models
Attribution models really fall into two main camps. Single-touch models give 100% of the credit to a single event, while multi-touch models spread that credit across several interactions along the way.
- •
First-Touch Attribution: This model gives all the credit to the very first interaction a prospect has with your brand. It’s perfect for early-stage startups whose main job is driving awareness and figuring out which channels bring fresh names into the database. But for a scale-up obsessed with pipeline velocity, it’s blind to every single nurturing step that actually turns a name into a qualified opportunity.
- •
Last-Touch Attribution: This is the most common—and most flawed—model out there. It gives all the credit to the final interaction right before a conversion. It’s great at telling you what closes deals, but it dangerously undervalues the content, ads, and events that created the opportunity in the first place.
This chart breaks down the core decision: are you looking for a single clue, or do you need the entire journey map?
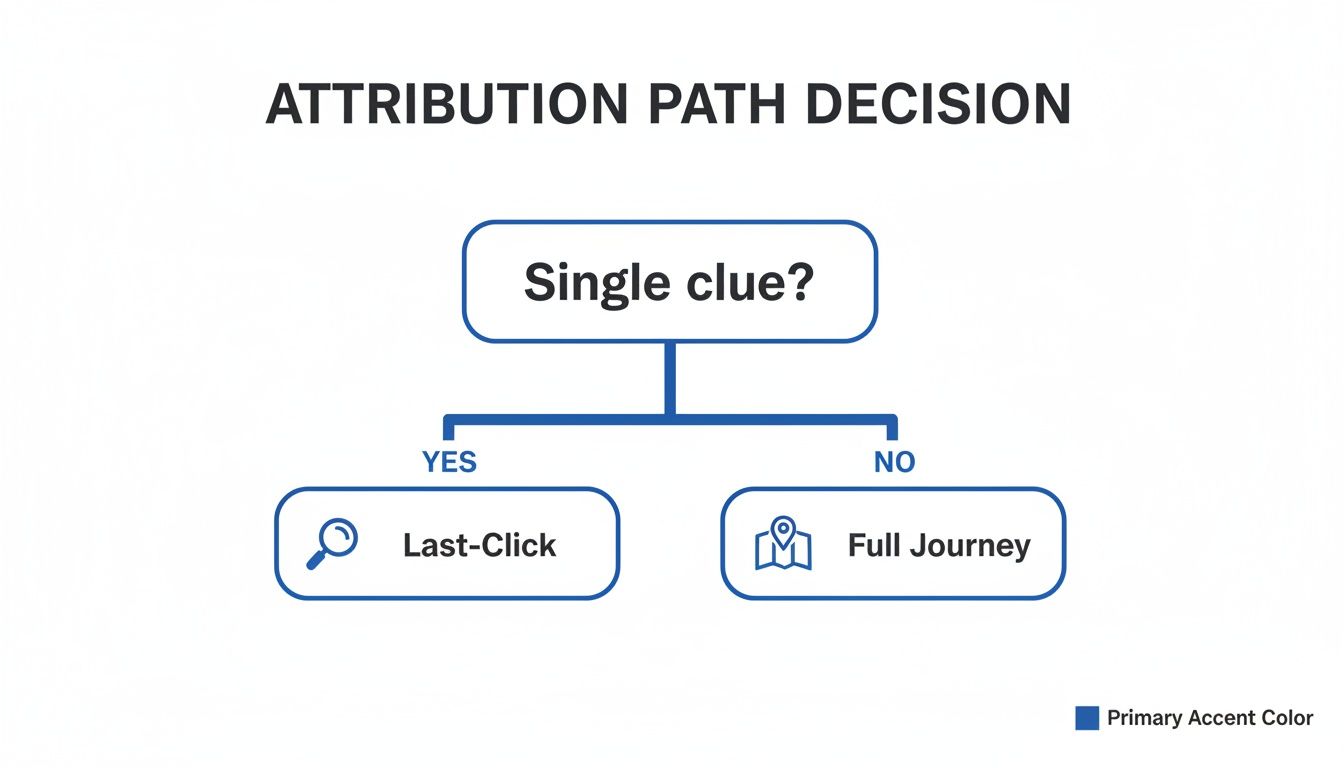
A flowchart illustrates attribution path decisions, asking 'Single clue?' leading to 'Last-Click' (yes) or 'Full Journey' (no).
The visual drives home a key point: while single-touch models offer simplicity, they provide a limited, often misleading, view of a complex B2B buying process.
Diving Deeper with Multi-Touch Attribution
For most scaling B2B SaaS companies, the truth lies somewhere between the first click and the last one. Multi-touch models acknowledge that a final decision is influenced by a whole series of interactions, giving you a much more balanced perspective.
If you're serious about optimizing your entire funnel, you need a clearer picture of what works at each stage. You can explore a deeper dive into these concepts in our guide to multi-touch attribution.
A HubSpot analysis confirms that a linear model, which assigns equal credit to every touchpoint, is best when you need a holistic view of all channel performance. It prevents you from over-prioritising one part of the journey at the expense of another.
This model is a solid starting point for most organizations. From there, you can explore more advanced models that assign different weights to the moments that truly matter in the buyer’s journey.
To make this easier, here’s a quick breakdown of the most common models B2B SaaS companies use.
Comparing Common Attribution Models for B2B SaaS
| Attribution Model | How It Works | Best For... | Biggest Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-Touch | 100% credit goes to the first interaction. | Early-stage startups focused on pure top-of-funnel demand generation and brand awareness. | Completely ignores every touchpoint that nurtures and converts the lead. |
| Last-Touch | 100% credit goes to the final interaction before conversion. | Teams who only care about what closes deals and need a simple, easy-to-implement model. | Dangerously undervalues the marketing efforts that created the opportunity. |
| Linear | Credit is split equally among all touchpoints in the journey. | Companies moving to multi-touch for the first time; getting a balanced, baseline view of the full funnel. | Treats a blog view and a demo request as equally important, which they aren't. |
| Time-Decay | Touchpoints closer to the conversion get more credit. | Businesses with long, complex sales cycles where recent interactions are more influential. | Can undervalue critical top-of-funnel activities that happened months ago. |
| U-Shaped | 40% credit to first touch, 40% to lead creation, 20% to middle touches. | Teams that prioritize both initial lead generation and the moment of conversion. | Gives less importance to the crucial mid-funnel nurturing that moves deals forward. |
| W-Shaped | 30% credit each to first touch, lead creation, and opportunity creation. 10% to the rest. | Orgs with a mature MQL-to-SQL process that want to credit key marketing and sales handoffs. | More complex to set up; requires clear, consistent milestone definitions in your CRM. |
This table shows a clear progression. As your GTM strategy gets more sophisticated, so should your attribution model.
Advanced Models for Complex Funnels
As your go-to-market strategy matures, you can adopt models that better reflect the nuances of your sales cycle.
- •
Linear Model: Simple and effective. Every touchpoint gets an equal slice of the credit. This is a great, balanced starting point for companies moving away from last-click for the first time.
- •
Time-Decay Model: This model gives more credit to interactions that happen closer to the conversion. It’s particularly useful for companies with longer sales cycles, as it correctly assumes that the demo request last week was more influential than the blog post read six months ago.
- •
U-Shaped Model: Also known as position-based, this model gives 40% of the credit to the first touch, 40% to the lead conversion touch, and spreads the remaining 20% across all the interactions in between. It’s perfect for businesses that value both initial lead generation and the specific action that creates a qualified lead.
- •
W-Shaped Model: This model takes it a step further. It assigns 30% of credit to three key milestones: the first touch, the lead creation touch, and the opportunity creation touch. The final 10% is split among the other interactions. This is a powerful model for organizations with a clear MQL-to-SQL handoff, as it properly credits those crucial marketing and sales alignment points.
Ultimately, choosing the right attribution model is about aligning your measurement with your business goals. Start simple—maybe with a linear model to get a baseline—and as your data maturity grows, test more advanced models that reflect the true complexity of your customer's journey.
How AI Is Revolutionizing Attribution Modeling
The rule-based models we've covered are a massive leap forward from the old last-click fantasy. But they still have one major limitation: they rely on a human making an educated guess about which touchpoints get the credit. The future of truly accurate, unbiased attribution is letting the data speak for itself.
That's where algorithmic attribution (also called data-driven attribution) comes in. Think of it less like a fixed rulebook and more like a smart, self-learning system. It uses machine learning to sift through thousands—or even millions—of customer journeys, analyzing both the paths that led to a sale and those that didn't. Instead of you telling the model what's important, it figures that out on its own.
Uncovering the Hidden Influencers
The real magic of AI in attribution is its knack for spotting powerful connections that a manual model would completely miss. A rule-based model is limited by your assumptions; an AI model has no such bias.
For example, an algorithmic model might reveal that prospects who download a specific technical whitepaper and later attend a particular webinar series are 5x more likely to convert to enterprise deals. A Linear or U-shaped model would never surface this kind of powerful insight. It would just smear a tiny fraction of credit across those events, completely burying their combined impact.
AI-powered attribution isn’t about replacing human intuition; it’s about amplifying the truth hidden within your data. It helps you shift from making good decisions to making mathematically optimal ones.
This level of insight moves your strategy from reactive to predictive. You’re no longer just reporting on what worked last quarter. You’re building a system that can forecast which mix of marketing activities will drive the best results next quarter. Our guide on AI-powered Revenue Operations digs deeper into how this data-first approach can transform your entire GTM strategy.
This screenshot shows an example of a Markov Chain model, a common method in algorithmic attribution. It visualizes the probability of a customer moving from one marketing touchpoint to another.

An Apple iMac displaying an AI-driven attribution network diagram on a wooden desk in an office.
Unlike simple models, this approach calculates the "removal effect" of each channel to determine its true contribution, giving you a much more nuanced and accurate picture of its value.
The Growing Demand for Algorithmic Precision
This shift toward data-driven models isn't just a niche trend; it's a global movement. Industry forecasts valued the global multi-touch attribution market at USD 2.43 billion in 2025, projecting it to hit USD 4.61 billion by 2030.
Within this market, algorithmic approaches already held a 34.8% share in 2024 and were forecast to expand at a ~14.3% CAGR as more brands ditch simplistic last-click rules to gain a competitive edge. You can discover more insights about this market growth on Mordor Intelligence.
For RevOps leaders, this isn’t just a tech upgrade; it’s a strategic necessity. Adopting AI for attribution modeling gives you the tools to make smarter, more profitable decisions at scale. It’s how you find the hidden revenue levers in your funnel and finally build a truly predictable growth engine.
Building Your Data and Tech Stack Foundation
An attribution model, no matter how sophisticated, is completely useless if it’s running on bad data. It's like a world-class chef working with spoiled ingredients—the final dish is guaranteed to be a disaster.
Your insights will only ever be as reliable as the data they’re built on. Before you even think about picking a model, you have to get your house in order. That means creating a single source of truth for every customer interaction. Without clean, unified data, you’re not doing attribution; you’re just creating expensive noise.

A tablet screen showing CRM, Marketing Automation, and Website Tracking, with a 'DATA FOUNDATION' note and office supplies.
The Non-Negotiable Tech Stack Components
To capture every touchpoint with any real accuracy, your tech stack needs to be tightly integrated and built for this exact purpose. There are three core pillars you absolutely can't compromise on:
- •A Centralized CRM: This is your command center. A robust CRM like Salesforce becomes the definitive record for every customer touchpoint, from sales calls to event attendance. It has to be the single source of truth that every other system feeds into.
- •Marketing Automation Platform (MAP): Tools like HubSpot or Marketo are non-negotiable for tracking digital engagement at scale. They grab the email clicks, form fills, and webinar registrations that make up the marketing half of the customer journey puzzle.
- •Website and Event Tracking: You need to see what users are actually doing on your digital properties. A Customer Data Platform (CDP) like Segment is perfect for this. It collects, standardizes, and routes event data from your site and product to all your other tools, keeping everything consistent.
Confronting Data Hygiene Head-On
Here’s a hard truth: the biggest hurdle isn't buying the tools; it's enforcing the processes that keep the data clean. Most attribution projects fail right here because of simple, avoidable mistakes.
The two most common culprits? Inconsistent UTM parameter usage and siloed data between sales and marketing. When UTMs are a mess, you have no idea which campaign drove a visit. When sales and marketing data don't talk, you lose the thread connecting a marketing lead to the eventual sales opportunity, breaking the attribution chain completely.
One of the most common gaps we find is a disconnect between perception and reality. A marketing leader might believe their UTM governance is 90% compliant, but a quick audit of the CRM often reveals it's closer to 30%. This is where revenue leaks.
Getting the architecture right is crucial for supporting any kind of sophisticated attribution. For a deeper dive, check out A Practical Guide to the Modern Data Stack.
A 3-Step Framework for Auditing Your Data Quality
To build a foundation you can trust, you need to diagnose where you stand today. Don't even think about implementing a new model until you've gone through this audit.
- •Map All Customer Touchpoints: Get a whiteboard and visually map every single way a customer can interact with your company. This includes everything from website visits and ad clicks to sales calls, trade show conversations, and support tickets.
- •Standardize Data Entry Protocols: Create a strict, non-negotiable rulebook for data entry. This means a rigid UTM naming convention (e.g.,
utm_campaign=Q3-Webinar-Series) and mandatory fields for sales reps to fill out in the CRM after every interaction. No exceptions. - •Implement a Data Governance Plan: Assign clear ownership for data quality. Who is responsible for monitoring CRM hygiene? Who audits UTM usage? Without someone's name next to these tasks, even the best protocols will fall apart.
This foundational work isn't glamorous, but it’s the only way to make sure your attribution efforts lead to real, measurable business outcomes instead of just a pile of confusing charts.
Your 6-Week Implementation and Validation Plan
An idea for a better attribution model is worthless until it's live and delivering value. This is where most projects die—stuck between a great concept and a messy reality.
To get you from theory to impact, here’s an actionable, six-week roadmap. We're breaking down the entire process into manageable sprints, sidestepping the usual traps like endless scope creep or data paralysis. This is how you build momentum and show results, fast.
Weeks 1-2: Data Audit and Tool Configuration
The first two weeks are all about the foundation. You can't build a reliable attribution model on messy, disconnected data. This phase is a full-on data audit to make sure your systems are capturing the ground truth.
- •Objective: Get a single, clean view of every customer touchpoint and lock down your data capture rules.
- •Key Actions:
- •Day 1-3: Map out every possible customer touchpoint. Think bigger than just ad clicks and form fills—include sales calls, webinar attendance, support tickets, and direct mail. If a customer can interact with it, it goes on the map.
- •Day 4-7: Dive deep into your CRM and Marketing Automation Platform. Hunt for the data hygiene gaps. Inconsistent UTM usage is almost always the biggest culprit here, so start there.
- •Day 8-14: Configure your tools to enforce the rules. Standardize UTM parameters across every team (no excuses!) and roll out a data governance policy with crystal-clear ownership.
Weeks 3-4: Model Selection and Historical Testing
Now that clean data is flowing, you can finally start playing with models. This phase is a dress rehearsal. You'll apply your chosen model to past data to see if the story it tells actually makes sense.
- •Objective: Choose your starting attribution model and stress-test its logic against your historical customer journey data.
- •Key Actions:
- •Day 15-18: Select an initial model that aligns with your business reality. A Linear model is a great, balanced start. If you have a well-defined MQL-to-SQL handoff, a W-Shaped model might give you a sharper view.
- •Day 19-28: Run that model against the last six months of closed-won deals. Do the results line up with what your team anecdotally knows to be true? Does it uncover any channels you've been undervaluing? Document every single finding. You can see how we put this validation process into practice in our own attribution model case study.
Your goal here is to establish a baseline. You need to know what "good" looked like under the old way of doing things. Without this historical benchmark, you have no way to prove your new model is actually better.
Weeks 5-6: Rollout, Training, and Validation
It’s go-time. This is where your model goes live, but the work isn’t over. The final phase is all about rolling it out, training your teams to trust this new source of truth, and defining the KPIs that will prove its value.
- •Objective: Successfully launch the model, drive team adoption, and define clear metrics for success.
- •Key Actions:
- •Day 29-35: Flip the switch. Roll out the attribution model and update your dashboards. Immediately schedule training sessions with both sales and marketing to walk them through what the new data means and—more importantly—how it should change their day-to-day decisions.
- •Day 36-42: Establish your validation KPIs. Your success criteria can't be fuzzy; they must be measurable and tied directly to revenue. For example: "Success = a 10% improvement in Marketing-Sourced Pipeline Velocity within the first quarter."
- •Ongoing: Don't set it and forget it. Schedule quarterly reviews to see how the model is performing. Your strategy will change, and your model needs to evolve with it.
This disciplined approach is what separates a nice-to-have analytics project from a strategic revenue driver. It's especially critical now, as investment in analytics continues to explode. The digital marketing analytics market in the MENA region alone was valued at USD 90.36 million in 2024, with projections showing growth over 18% CAGR as businesses demand measurable ROI. If you're interested in these regional trends, you can explore the market research.
By following this plan, you can expect to see a 15–25% improvement in pipeline velocity within 6 weeks as you start reallocating budget to what’s actually working.
Common Mistakes That Invalidate Your Attribution Data
You can have the perfect model and the ideal tech stack, but a few simple, avoidable mistakes can render your attribution data completely useless. Getting this wrong doesn't just mean you're flying blind; it means you're actively making expensive decisions based on flawed information.
Think of this as the diagnostic checklist every RevOps leader needs. Let’s pinpoint the most common—and costly—errors that poison your data and walk through exactly how to fix them.
Ignoring Offline and Sales Touchpoints
One of the biggest blunders is focusing exclusively on digital marketing interactions. What about that crucial conversation your AE had at a trade show? Or the sales-led lunch that finally moved a deal forward? When these touchpoints aren't captured, your attribution model is only seeing half the story.
According to HubSpot, interactions like a Call connected or Attended marketing event are vital for accurate attribution. If they aren’t logged, your model will mistakenly give 100% of the credit to the last marketing email someone clicked, totally ignoring the sales effort that actually got the deal signed.
The Fix: A Framework for Offline Tracking
Don't just tell your team to "log offline events." That never works. Instead, give them a dead-simple system that fits right into their existing workflow.
- •Create Unique Campaign Codes: For every event (conference, webinar, dinner), create a unique, memorable code like
SAASCONF24. - •Arm Your Sales Team: Get these codes to your sales reps before the event. Put it in their calendar invite, their travel docs, everywhere.
- •Mandate CRM Logging: Make it mandatory for AEs to log every significant interaction from that event in your CRM, attaching that specific campaign code. This creates a direct link between the offline activity and the contact and opportunity records, finally closing the data gap.
Failing to Account for Long B2B Sales Cycles
In B2B SaaS and Fintech, sales cycles aren't measured in days; they're measured in months, sometimes even years. A First-Touch model might credit a blog post someone read 18 months ago, while a Last-Touch model credits the final demo request. Both are dangerously incomplete.
The reality is that dozens of influential touchpoints happen in between—nurturing emails, follow-up calls, case study downloads, you name it. Ignoring them is like watching only the first and last five minutes of a movie and trying to guess the plot. You'll get the ending, but you'll have no idea why it happened.
A common diagnostic finding is that sales leaders believe their team follows up on 80% of high-intent leads within 24 hours. The CRM data, however, often shows the reality is closer to 25%. This is a massive gap where attribution and revenue fall apart.
Misinterpreting Correlation for Causation
This is a subtle but absolutely critical error. Your attribution data might show that prospects who download your "Ultimate Guide" whitepaper are highly likely to close. Great! So, you pour more money into promoting the whitepaper.
But what if that guide is something prospects only seek out after they've already decided to buy and are just doing their final due diligence?
In this case, the whitepaper isn't causing the conversion; it's simply correlated with late-stage buyer intent. Over-investing here would be a total waste of resources. True attribution separates the actions that influence decisions from those that merely accompany them. This is where algorithmic models shine, as they are designed to sniff out the true causal relationships in your data, moving you from guesswork to predictable outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions About Attribution Modeling
Got questions? You’re not the only one. Attribution modeling can feel like a maze, but getting straight answers is what separates a confusing dashboard from a clear path to revenue. Here’s what RevOps leaders really need to know.
How Often Should We Review or Change Our Attribution Model?
You should be reviewing your attribution model quarterly, but only consider changing it annually or after a major business event. Think a big go-to-market shift, launching in a new market, or a major product pivot.
Why the distinction? Consistency is king for benchmarking performance. A quarterly check-in lets you validate if the model still reflects your customer journey without overreacting to a single campaign’s weird results. But constantly switching your model creates noisy, unreliable data, making it impossible to see if you're actually making progress.
What Is the Biggest Challenge When Implementing Attribution Modeling?
Hands down, the single biggest challenge is poor data quality. Inaccurate, inconsistent, or just plain incomplete data is the #1 reason attribution models fail to deliver anything useful.
This mess usually comes from sloppy UTM tracking, sales teams not logging calls and meetings in the CRM, and data being trapped in disconnected platforms. Forget about fancy algorithmic models for a minute. Your first job is to build a rock-solid process for capturing clean, standardized data at every touchpoint. Without that foundation, your model is built on sand.
Does Attribution Modeling Work for a Company with a Long Sales Cycle?
Yes, and in fact, it’s more critical for companies with long sales cycles of 6-18 months. Simple models like Last-Touch are completely useless here. They ignore the dozens of crucial interactions that happened over many months and give you a dangerously incomplete picture.
This is exactly what multi-touch models like Time-Decay, W-Shaped, or a custom model are built for. They make sure the early-stage activities that started the conversation—that first whitepaper download or webinar—get the credit they deserve. This gives you a far more accurate view of what actually influences a complex, long-term buying decision.
Ready to move from theory to a validated growth strategy? Learn how the 6-Week Revenue Growth Sprint applies this framework to your business. We help SaaS leaders implement systems that show what’s actually working, unlocking 15-25% improvement in pipeline velocity. Learn more at https://altiorco.com.


